Business Rules
Anatomy of a Business Rule
This section provides a detailed explanation of the following:
-
Business Rule structure and fundamentals
-
Business Rule Classifications
-
Specific Business Rule Types
-
Business Rule organization
-
OneStream Business Rule framework
-
Best practices for Business Rule architecture
Business Rule Definition
A Business Rule is a class, meaning each business rule is an independent object encapsulating code written in either VB.Net or C#. A business rule can be a one-line call to write a log message, or it can be a full code library containing other custom classes, methods and properties.
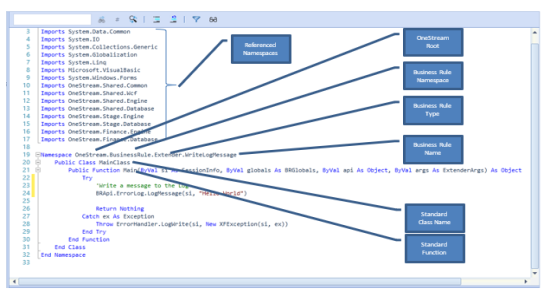
Each OneStream Business Rule has a predefined Namespace, a Public Class and a Public Function that the OneStream platform engines invoke when the Business Rule needs to be called.
NOTE: There are two broad Business Rule Classifications: Shared Business Rules and Item Specific Business Rules. Shared Business Rules can be written in either VB.NET or C#, Item Specific Business Rules can be written in VB.NET only. All code examples presented in this guide will be shown in VB.NET.
Predefined Object Names
-
Namespace: OneStream.BusinessRule.<Business Rule Type>.<Unique Business Rule Name>
-
Class: MainClass;
-
Function: Main
Example Business Rule Structure
Function Prototypes
Each Business Rule has one standard entry point Function Title called Main. The Function definition below represents the standard prototype used by the Main Function in each OneStream Business Rule. The Main Function always has the same standard parameter layout, but the last two parameters, API and ARGS, contain different object references based on the type of Business Rule being executed.
Public Function Main
(
ByVal si As SessionInfo, Connection Object Required to use API
ByVal globals As BRGlobals, Global Variable Object Used to Share Values
ByVal api As Object, Specific API object (Different for each Type)
ByVal args As ExtenderArgs Specific Arguments (Different for each Type)
)
As Object